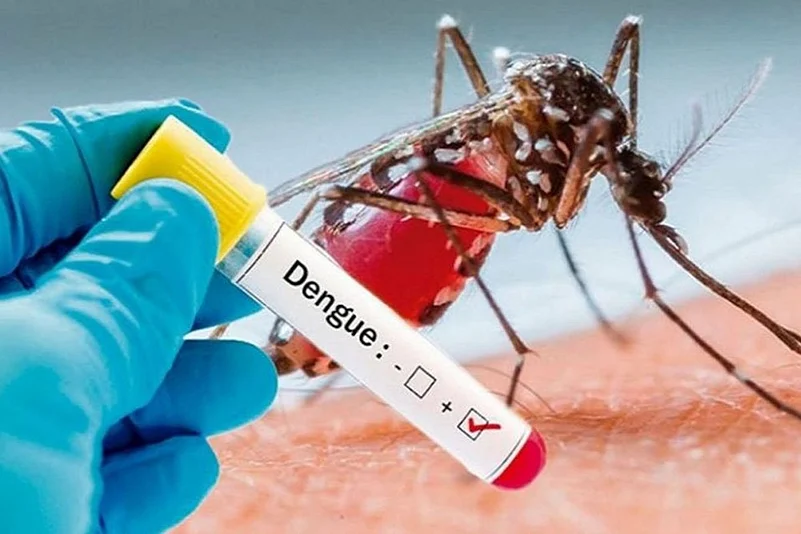
The fear of dengue has gripped people across the states. Health Department officials said that though a large number of people are suffering from viral fevers, they are rushing to hospital suspecting dengue. However, you cannot ignore dengue fever thinking it’s just viral fever.
The two are vastly different from one another. Initially, it can be difficult to know what exactly you are suffering from – the initial symptoms may be the same, there are some noticeable distinctions in the way that they occur.
What is viral fever?
Viral fever lasts for three to five days, accompanied by severe chills and body ache. It is usually transmitted through the air by droplets from infected people, or by touching infected secretions.
What is dengue fever?
Dengue fever, on the other hand, is transmitted by the tiger mosquito (Aedes Aegypti). The mosquito has black and yellow stripes and typically bites in the early morning or at dawn. The virus enters and reproduces in white blood cells.
Symptoms
Many people experience no signs or symptoms of a dengue infection.
When symptoms do occur, they may be mistaken for other illnesses — such as the flu — and usually begin four to 10 days after you are bitten by an infected mosquito.
Dengue fever causes a high fever — 104 F (40 C) — and any of the following signs and symptoms:
- Headache
- Muscle, bone or joint pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Pain behind the eyes
- Swollen glands
- Rash
Severe dengue happens when your blood vessels become damaged and leaky. And the number of clot-forming cells (platelets) in your bloodstream drops. This can lead to shock, internal bleeding, organ failure and even death.
The warning signs usually begin the first day or two after your fever goes away, and may include:
- Severe stomach pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Bleeding from your gums or nose
- Blood in your urine, stools or vomit
- Bleeding under the skin, which might look like bruising
- Difficult or rapid breathing
- Fatigue
- Irritability or restlessness
When to see a doctor?
Seek immediate medical attention if you've recently visited an area in which dengue fever is known to occur, you have had a fever and you develop any of the warning signs. Warning signs include severe stomach pain, vomiting, difficulty breathing, or blood in your nose, gums, vomit or stools.
If you've been traveling recently and develop a fever and mild symptoms of dengue fever, call your doctor.
Risk factors
You have a greater risk of developing dengue fever or a more severe form of the disease if:
You live or travel in tropical areas. Being in tropical and subtropical areas increases your risk of exposure to the virus that causes dengue fever.
You have had dengue fever in the past.
Complications
Severe dengue fever can cause internal bleeding and organ damage. Blood pressure can drop to dangerous levels, causing shock. In some cases, severe dengue fever can lead to death.
Women
Women who get dengue fever during pregnancy may be able to spread the virus to the baby during childbirth. Additionally, babies of women who get dengue fever during pregnancy have a higher risk of pre-term birth, low birth weight.