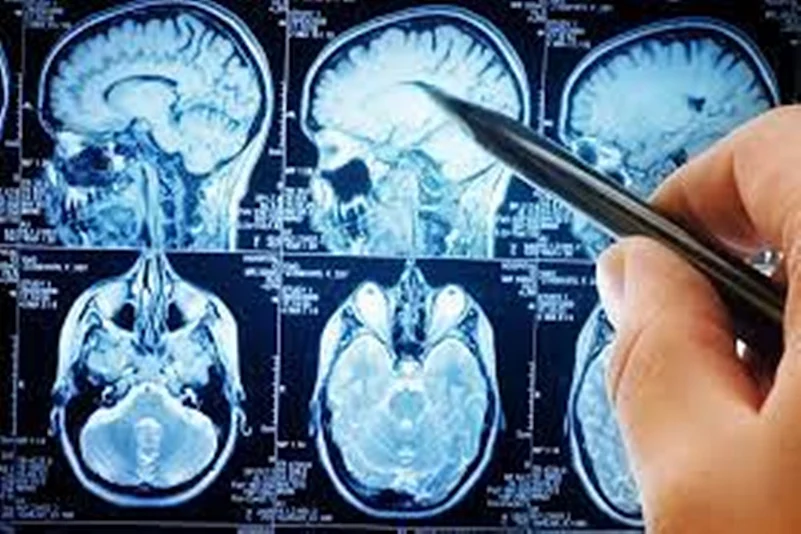
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain. There are many types of brain tumors. Some are noncancerous (benign), while others are cancerous (malignant). Tumors that originate in the brain are more common. When cancer spreads from other parts of the body to the brain, it is called a secondary, or metastatic brain tumor. Although brain tumours can happen to anybody, there are certain risk factors that increase risks such as age, gender, family history of the disease, exposure to infections, chemicals, radiations, and harmful toxins, head injuries, and seizures. Early detection of the disease can positively impact the overall success and survival rate in patients. Therefore, there needs to be awareness around the signs and symptoms of brain tumours for timely diagnosis and management of the condition.
The growth rate, size, and location of the tumor determine its effect on the function of the nervous system. The same factors also determine the signs and symptoms even though sometimes, the signs may significantly vary. In some cases, the symptoms may typically stem from a different underlying neurological or brain disorder.
Below are 8 signs and symptoms that may indicate a brain tumor:
1. Seizures: Fits or seizures can be the first sign of a brain tumor. A significant proportion of patients diagnosed with a brain tumor experience these. It can cause abnormal movements in the body and may lead to loss of consciousness. They may also be accompanied by flashes of light or other visual, sensory, etc. disturbances.
2. Decline in the brain’s functioning: Memory loss and the inability to concentrate or focus on usual activities is a matter of concern, inability to perform routine executive functions of the brain like calculation, reasoning, routine household work requiring planning (e.g. making tea, food) could be a sign of a developing brain tumor.
3. Severe, persistent headaches: If a headache is persistent, especially more in the mornings, and does not cure with over-the-counter medication, it may be a sign of warning and requires an expert opinion. If these headaches are followed by double vision, nausea, and vomiting, numbness, or weakness, it may be an alarming symptom.
4. Speech problems: A sudden change in speech, like stuttering and not able to recall or pronounce words, may be a potential symptom. Especially when a brain tumor affects the speech area of the brain.
5. Weakness: A person with a brain tumor will not be able to function as efficiently with their arms and legs. They may also experience some clumsiness and loss of balance while walking.
6. Loss of vision: Bitemporal hemianopsia is a condition of temporary blindness where there is no vision in the outer half of both the right and left of the visual field.
7. Changes in personality: A brain tumor can alter the nature of judgment in individuals, and he or she may experience agitation, mood swings, etc.
8. Hearing problems: One may experience a constant ringing sensation in their ears, which may eventually lead to loss of hearing ability.
Other brain tumor symptoms include altered taste perception, obesity, and hand tremors. Since most of the symptoms of a brain tumor may overlap with many other conditions, it is crucial to get an accurate diagnosis by a doctor.
If it's suspected that you have a brain tumor, a number of tests and procedures may be recommended, including NCCT/ MRI brain, PET Brain, Brain.
The treatment for the brain tumor depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor. Surgery is the primary modality of treatment of most brain tumor especially if large in size, creating problem as causing deficit or if it is malignant. The aim is total removal of the tumor without causing any fresh deficit. For malignant brain tumor, even if we remove all the visible tumor, residual tumor cells may persist in the depth which is not visible even with the microscope. These would need to be treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy – which for brain tumors is usually a tablet and is easily tolerated. Not all tumors need surgery though and some small brain tumors can be treated with CyberKnife radiosurgery – which is the non-invasive delivery of highly focused radiation beams onto the tumor without opening the head. This is also used for small residual tumors after surgery and for recurrent tumors.
Timely detection, as well as a proper brain tumor treatment, can work in favour of the patient and can expedite the progress towards a tumor-free life.
(Dr Vinay Goyal. MD, DM, (AIIMS), FIAN is also the Director - Neurology Institute of Neurosciences, Medanta)